Sunday, July 1, 2012
Tuesday, May 15, 2012
The Cell Cycle in Pictures
The overall process
The cell cycle describes the typical cycle of a somatic cell that will go through mitosis.
Mitosis is divided into 4 phases:
Prophase:
-chromatin condenses to chromosome
-nuclear envelope disintegrates and disappears
-spindle forms
Metaphase:
-chromosomes line up at the equator
Anaphase:
-chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
Telophase:
-cell plasma divides
-nuclear envelope reappears
 |
| The Cell Cycle (Photo credit) |
Mitosis is divided into 4 phases:
Prophase:
-chromatin condenses to chromosome
-nuclear envelope disintegrates and disappears
-spindle forms
Metaphase:
-chromosomes line up at the equator
Anaphase:
-chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
Telophase:
-cell plasma divides
-nuclear envelope reappears
The lac Operon
 |
| Photo credit |
An operon is a cluster of bacterial genes along with an adjacent promoter that controls the transcription of those genes.
When the genes in an operon are transcribed, a single mRNA is produced for all the genes in that operon. This mRNA is said to be polycistronic because it carries the information for more than one type of protein.
What is the the lac Operon?
What is the the lac Operon?
The lac operon is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and some other enteric bacteria.
Labels:
Molecular Biology
The 20 Amino Acids
This is the basic structure of an amino acid
Here are the 20 amino acids
 |
| Structure of an Amino Acid (Photo credit) |
Here are the 20 amino acids
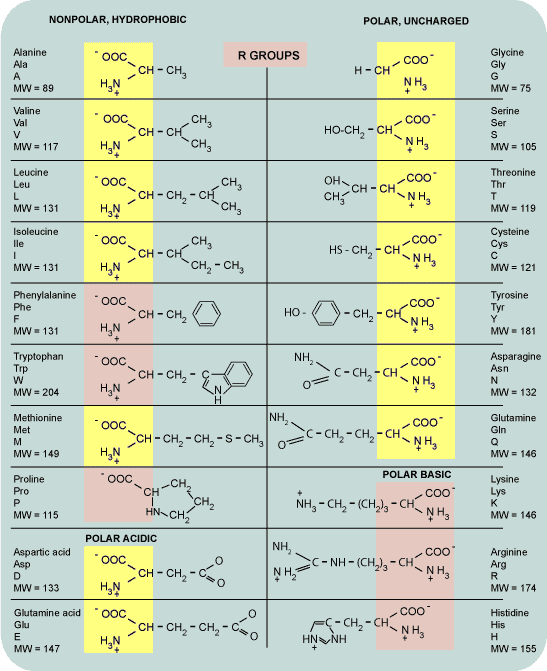 |
| Amino Acids (Photo credit) |
Labels:
Biochemistry,
Macromolecules
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in a Glance
Photo credit
Photo credit
A very good animation is given below
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vmlLj1aLZ7s&feature=related
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence.
Developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis, PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical and biological research labs for a variety of applications
Photo credit
A very good animation is given below
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vmlLj1aLZ7s&feature=related
Labels:
Molecular Biology





